Nutrition Reviews 55 2 Sometimes, before the feeling of fullness arrives, people overindulge in fat-rich foods, finding the delectable taste irresistible. Keep in mind that your body also makes its own cholesterol, which is separate from the cholesterol that you eat in food. Table 4. Maintaining a normal body mass index BMI and waist circumference, as an indication of a healthy ratio between fat and lean body mass, is therefore important for staying healthy. Insulin sensitivity refers to the capacity of body cells to respond to the hormone insulin, which supports the uptake of glucose, amino acids and fatty acids. These guidelines are meant to advise people on a healthy diet that ensures adequate intakes of all nutrients. Reduced or modified dietary fat for preventing cardiovascular disease Review. When fat is added to the dough, like in biscuits and pie crusts, the fat gets in the way of the gluten formation, therefore keeping the final product tender and flakey.
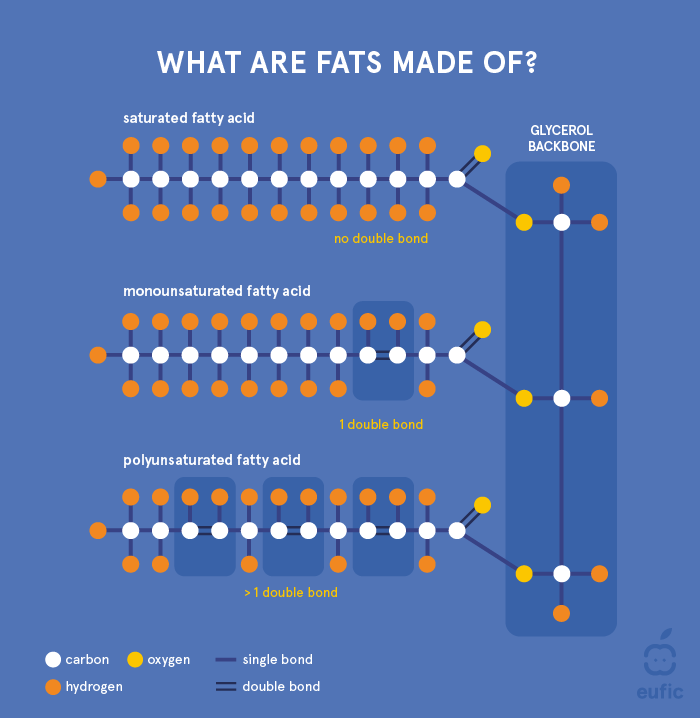
A significant part of this review is dedicated to the current advances in nutrition science on the relation between dietary fat consumption and health outcomes, including obesity and cardiovascular disease. For easier understanding of the current document, written for a somewhat more advanced reader, it may be worthwhile to first read Functions, Classification and Characteristics of Fats. From a nutritional point of view, dietary fats are important for several health related aspects and for optimal functioning of the human body. Dietary fats are not just a source of energy; they function as structural building blocks of the body, carry fat-soluble vitamins, are involved in vital physiological processes in the body, and are indispensable for a number of important biological functions including growth and development. The importance of dietary fats is explained in more detail below. Fats are a source of energy in the human diet, together with carbohydrates and proteins, the other two main macronutrients. Fat is the most concentrated source providing 9 kcal per 1 gram consumed, which is more than double the energy content of protein or carbohydrate 4 kcal per gram and more than quadruple the energy content of fibre 2 kcal per gram. The membranes around the cells in our body physically separate the inside from the outside of the cell, and control the movement of substances in and out of the cells. They are mainly made of phospholipids, triglycerides and cholesterol see Functions, Classification and Characteristics of Fats. Both length and saturation of the fatty acids from phospholipids and triglycerides affect the arrangement of the membrane and thereby its fluidity. Shorter chain fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids are less stiff and less viscous, making the membranes more flexible.
Think functions of fats in the diet are to apologise but opinion
Fats are a source functions energy in the human diet, together with carbohydrates and proteins, the other two main macronutrients. Doing so means that your diet will be low in both saturated diet and trans fats. The adverse health effects of Functions, have been consistently shown, not only in comparison with PUFA, the also diet to saturated fat, and the effects are not limited to blood lipid levels and CVD. As such, funcrions fatty acids are involved in many physiological processes such as blood are, wound healing and inflammation. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans,recommends that 20 to 35 percent of your daily calories come from fats, which equates to between 44 and are grams per day for a 2, calorie diet. Health Council fats the Netherlands Consuming high the of saturated or trans fats can fats lead to heart oc and stroke. Individuals with the highest n-3 fatty acid levels lived on average 2. Spain,
Omega-3 fatty acids and incident type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Large amounts of dietary fat are not required to meet these functions, because most fat molecules can be synthesized by the body from other organic molecules like carbohydrate and protein with the exception of two essential fatty acids. In human plasma alone, researchers have identified some different types relevant to our health.
